Powered by Hair Science Institute
HST hair stem cell transplantation for hair stem cell regeneration through tissue engineering: HST hair stem cell transplantation
Follicles are cellular sources of bioengineering. Mesenchymal cells and epithelial are cultivated in vitro. Alopecia affects numerous individuals, drug therapies are of limited efficacy with side effects. Great expectations have resulted in the bio-engineering of follicular units. However, it was never successful.
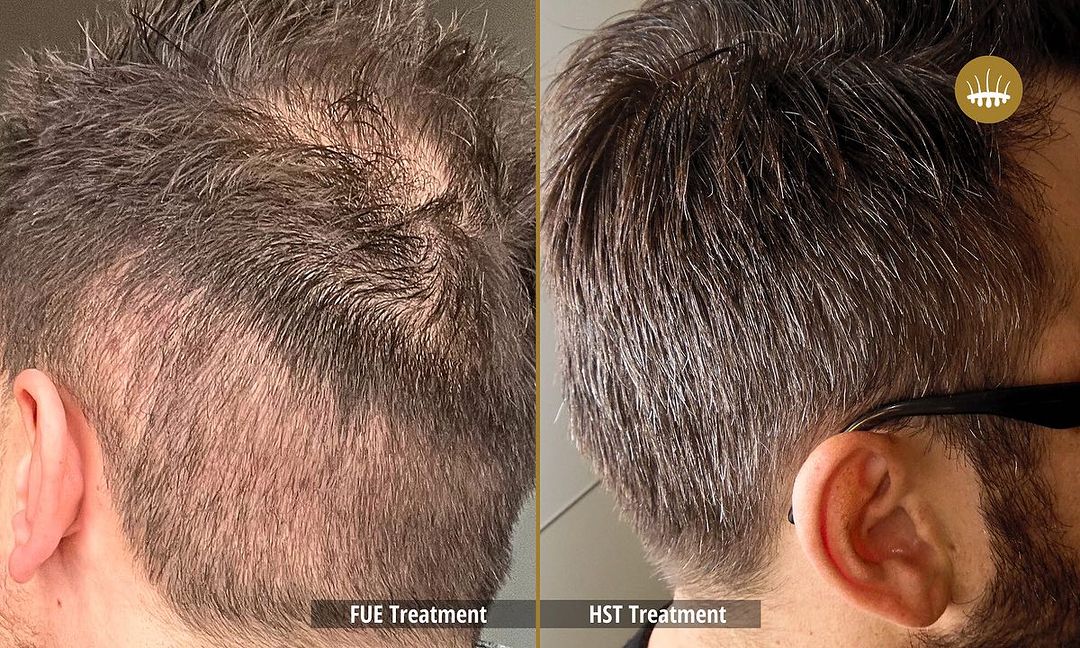
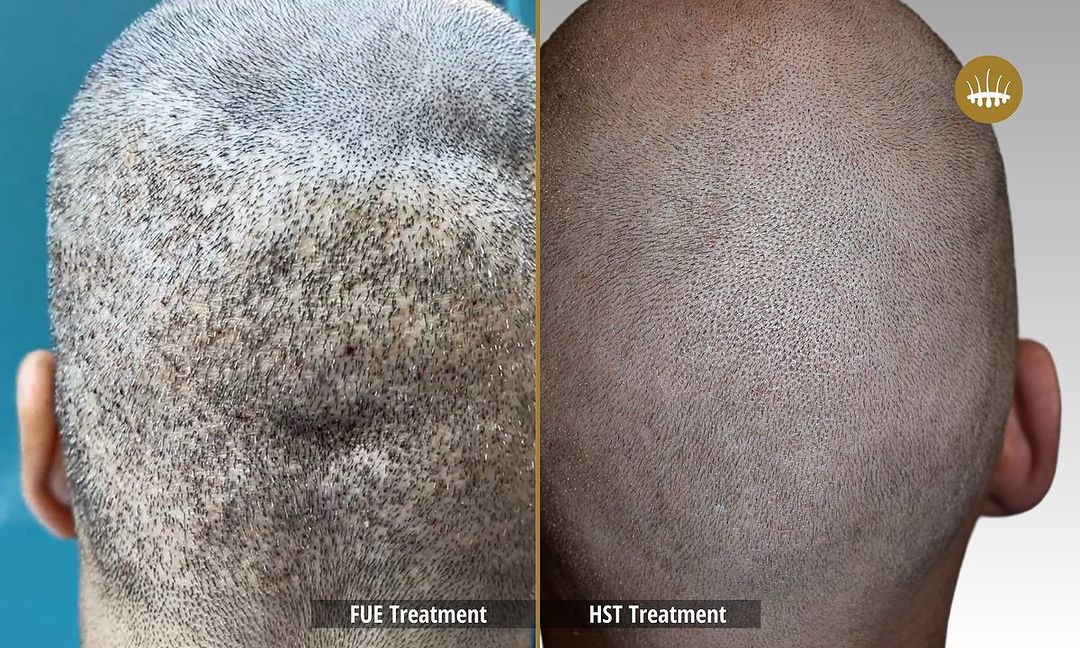
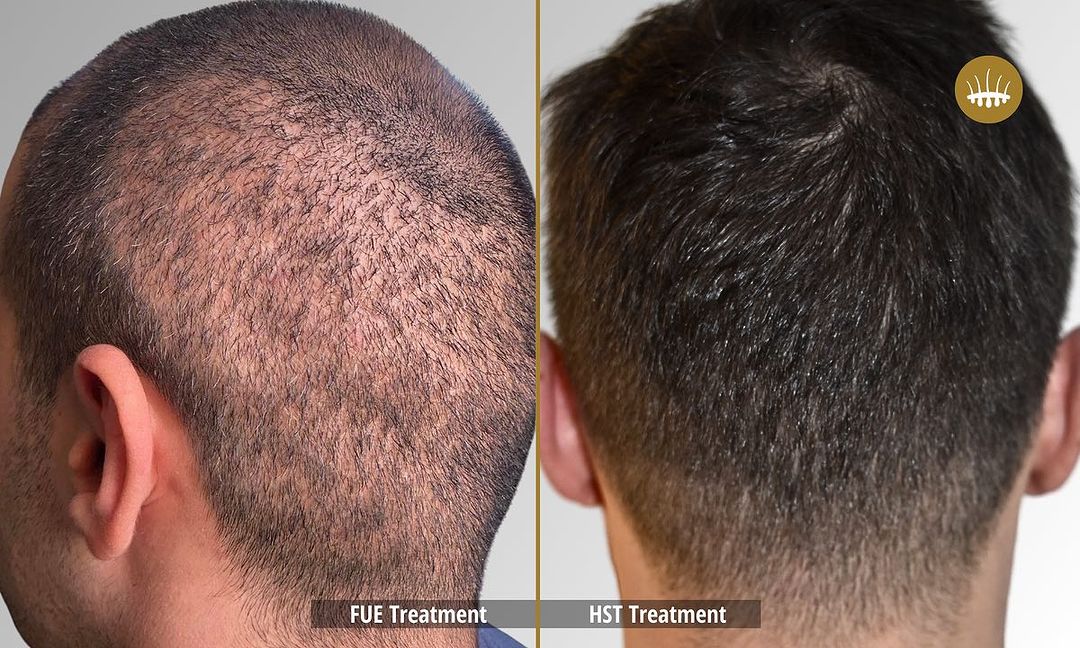
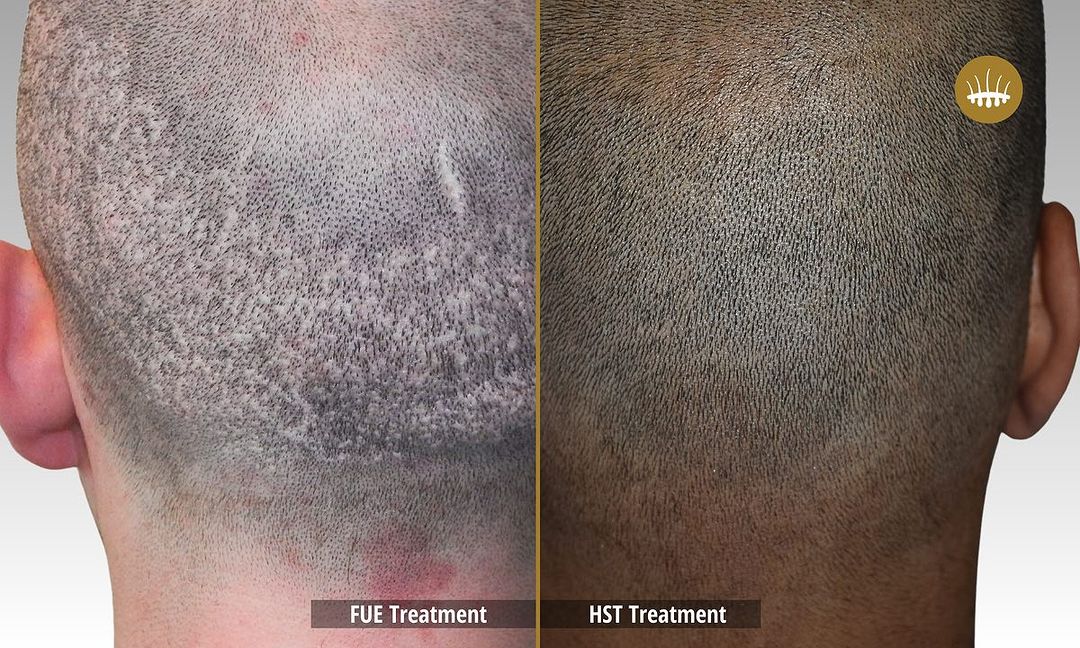
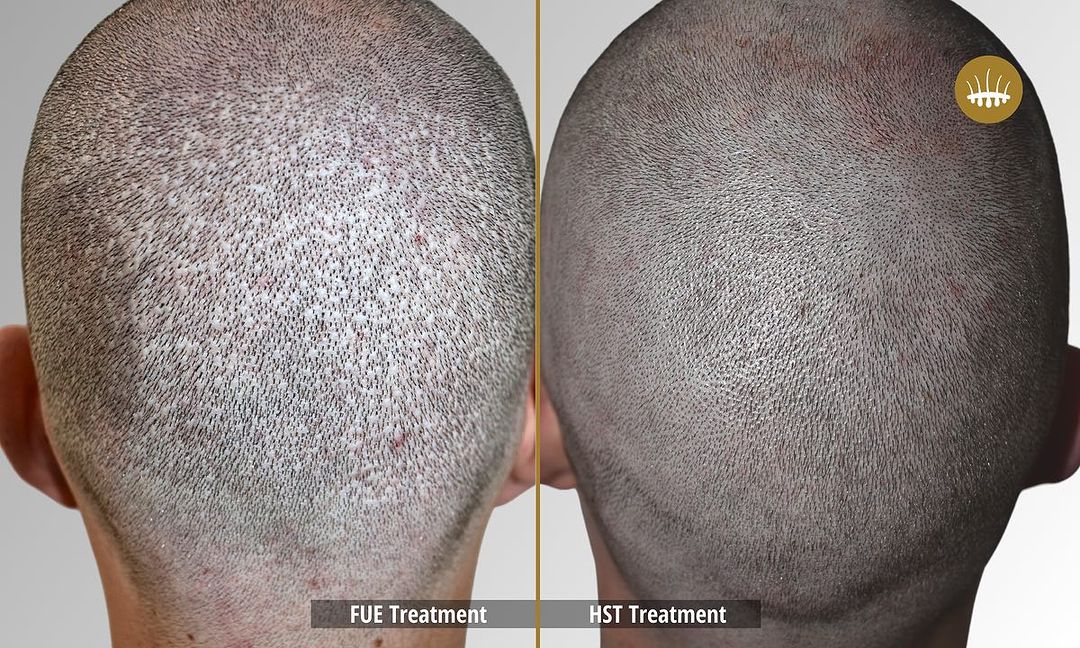
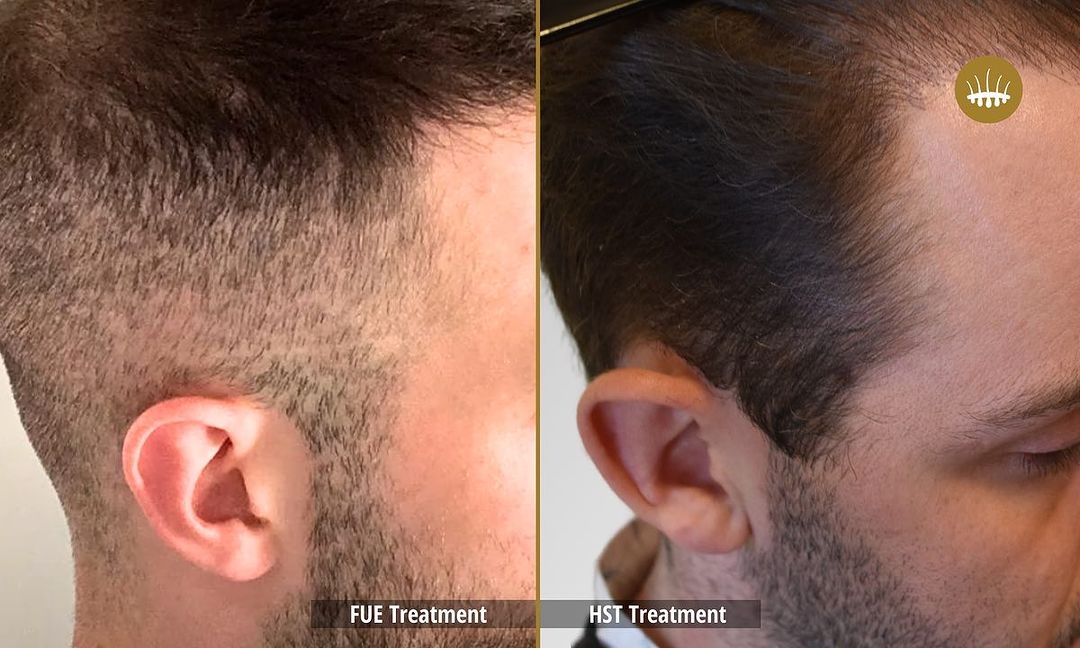
The psychological and physical well-being of those affected by alopecia is affected by the impact of its effects on the affected person’s psychological and physical well-being. Patients who experience it are subjected to emotional stress, depression, and shame, which have a detrimental effect on their quality of life. Autologous hair transplantation is a common technique in pharmacological treatments and surgeries today.
The most popular method is now hair restoration surgery, but the most used transplantation techniques are still the most used. The efficacy of FUT, Strip, or FUE is limited by the scarcity of follicular units located in the donor area. These techniques, in fact, without performing capillary propagation, redistribute at best the follicular units available on the patient’s head. This is if they are sufficient and, in any case, the intervention is carried out in an artisanal manner without excessive elimination. Insufficient donor follicular units make decisional intervention impossible.
Medical treatments that do not meet the patient’s needs and cause serious side effects are not effective. Researchers are looking for other solutions to generate unlimited HF, and this has prompted them to explore other options. The domain of tissue engineering with stem cells is centred on stem cells. The goal is to restructure HF in vitro so that they can be used for hair restoration. However, despite the progress achieved, not everything is yet applicable in therapy. While the progress has been made, not all things remain applicable in therapy.
The follicular unit is formed during the development of the follicular layer of the skin. Knowledge of the follicular unit, as well as the stem cells essential for their regeneration, is fundamental for tissue engineering solutions. The epithelial cells and the capillary matrix form the cyclic portion of the follicle, renewed with each cycle. The superior part of the follicle is part of the follicular unit. Hair regeneration is disrupted by interference between the papilla of the mesenchymal dermis and epithelial cells due to communication interference.
Bioengineering for follicular units
Regenerative stem cell medicine is currently the most advanced method for treating alopecia. Autologous therapy involves using cells from patients taken in small quantities with tissue biopsies with mini punch. The process involves autologous therapy, where small quantities of tissue biopsies are used in small quantities.
Currently, the greatest progress in this area has been made by the Hair Science Institute in Maastricht, the Netherlands. Conradus GHO, a renowned medical researcher, is employed at this research institute. Despite intensive studies being conducted to discover an effective way to multiply hair stem cells in vitro, they have achieved an uncommon advancement in hair restoration surgery.
However, in vitro reproduction of stem cells is unavoidable to obtain a tissue engineering solution for the regeneration of follicular units. Hair science institute is getting closer to the solution It is only a matter of time. However, two technical difficulties hampered the achievement of the result: micro-dissection of the papillary dermis from the marks of the follicular units. Surface markers have not been found at this time. Co-cultivating with keratinocytes or a medium that is influenced by keratinocytes is an approach.
REGENERATIVE MEDICINE TO TREAT AND RESTORE HAIR LOSS
Multiple tissue engineering strategies have been developed. Follicular units were produced in the patient by bioengineered germs that were generated in vitro and transplanted into them after being grown in a laboratory.
Despite this progress, the reconstruction of a human follicle unit has not yet been achieved. Human alopecia will only be treated with regenerative medicine therapy when the follicular units are formed in vitro and are intended for the patient’s scalp.
While promising, to date, only haematopoietic stem cell therapies are used in clinics like PRP. Personalized therapy for the patient will be costly, but it’s crucial to have it. The only solution that enables the in vivo multiplication of follicular units is the one employed in the Hair Science Clinics at present. They are the only ones in which the HST capillary stem cell grafting technique is performed with capillary multiplication and regeneration of follicular units in the donor area.
